Active Debug Port
The Active Debug Port
The Active Debuggers capture detailed debug information about the execution of firmware, including the graphed values of variables and the exact timings of debug messages as they are executed. The debug information is output from the microprocessors using the firmware routines below using a single line of code to create the Active Debug Port using standard GPIO pins (1 or 2 pins) or a standard SWV port. See the bottom of this page for the active.c and active.h files to include in your firmware projects.
There are 2 types of data captured over the Active Debug Port: ACTIVE Text and ACTIVE Value (as well as the standard logic and analog inputs).
ACTIVE Text is character strings and are identical to traditional "printf" output. They are graphed over time as well as listed vertically.
Each debug text output is created by a simple source code line such as:
ACTIVEText( 2, “Button Pressed” );
or
ACTIVEprintf( 2, “%d”, accum );
ACTIVE Value is value data that is then graphed versus time for a visual representation of the data.
Each data point on the waveform is created by a simple source code line such as:
ACTIVEValue ( 3, myvariable );
The label on the left of each waveline can also be set from your firmware by calling the ACTIVELabel function.
Active Debug Port Protocol
The Active Debug Port Protocol is sent from an embedded processor to the ACTIVE Debugger Pod to transfer the information from the embedded system to the computer for capture and display.
The data is sent from the embedded processor to the ACTIVE Debugger Pod using the ACTIVE Debug Port, which is available in 3 versions, 1 wire or 2 wire versions and an SWV version (Active-Pro only). Each version of the bus sends the same byte stream.
The 1 Wire ACTIVE Debug Port uses an ASYNC serial UART bus signaling with 8 data bits and no parity at any baud rate that is an exact divide down of 30MHz. Bit alignment is defined by the UART start bit protocol.
The 2 Wire ACTIVE Debug Port uses a SYNC serial bus signaling (CLOCK and DATA lines) with 8 data bits with DATA sampled on the rising edge of the CLOCK rate up to 80M bits per second. This mode can be created easily using an SPI bus using just the SCK and MOSI signals. The bit alignment is determined by the fact that every MSBit is a 0. To sync we detect if the MSBit is a 1, and if it is we skip a bit until it is never a 1. Once synced, it will remain synced until the 0x7F no longer exists of an MSBit is a 1, and a new sync procedure will be completed.
On the Active-Pro, the SWV ACTIVE Debug Port uses the UART encoding mode of SWV (Manchester is not supported) with serial UART bus signaling with 8 data bits and no parity at any baud rate that is an exact divide down of 30MHz. Bit alignment is defined by the UART start bit protocol. SWV outputs 2 bytes for each transmitted character: the first byte is the SWV channel and type indicator, and the second byte is the actual channel data. The Active Debug Port data is contained in these second bytes and the first bytes are ignored.
Active Value Packet Format
The packet format on the Active Bus to send values (as in the ACTIVEValue() routine below) is as follows:
Active Text Packet Format
The packet format on the Active Bus to send debug text (as in the ACTIVEText() or ACTIVEprintf() routines below) is as follows:
Best Practices
Until we can get an Active Debug Port Hardware Block built inside every microprocessor, use the following Best Practices while using these critical new debug ports on any of your microprocessors:
Debug Output Speed - Since each call to the debug output takes a small amount of time away from the host processor, it is important to use the fastest method of transfer possible. The fastest mode is 2-wire mode, and if you have a built in SPI hardware block in your MCU even better. The slowest mode is typically the 1-wire mode since it is typically driven by a UART. In this case, use as fast a baud rate as possible.
Volume of Debug Messages - To minimize the impact on your host processor and to minimize the capture file size, try to have debug messages only when needed, and make them as brief as possible while not losing the context of the message.
Turn Off Digital Signals- Although you can capture the Digital signals that make up the Active Debug Port, it is not necessary, and if enabled will consume far more data bandwidth than with them off. So Turn off the Digital Input channels for your Active Debug Ports (and any other hardware decoded busses as well).
Where is the First Debug Output Message? - There is auto signal detection that automatically determines which signal is clock and which is data. This process takes a whole byte to determine, so it has a 50% chance of misinterpreting the first byte. To solve this, and capture the very first message, either send the message again, or swap the wires to get the very first message. Once the Active-Pro determines the correct signal setup (clock and data detection), it will be correct for future captures.
Using these methods, you can have a powerful debug port into your microprocessor with minimal impact on your application firmware.
ACTIVEValue ( 25, 89815 ); using 2-wire mode with a 33MHz SPI hardware block consumes 1.75usec
ACTIVEText ( 24, “Hello” ); using 2-wire mode with a 33MHz SPI hardware block consumes 2.88usec
Firmware Routines
The Active-Pro™ captures the debug data from your firmware when you call the following routines.
ACTIVEText ( unsigned char channel, unsigned char * string );
This routine outputs the given text on the Channel specified.
channel = 0 thru 63
string is the \0 terminated string to output. These can also be special Control Commands (below) to control various features of the host capture software.
Example: ACTIVEText ( 2, "It Happened!"); // Displays "It Happened!" on channel 2 at the current time
ACTIVEprintf ( unsigned char channel, unsigned char * printfformatstring, ... );
This routine outputs the printf-like text on the Channel specified.
channel = 0 thru 63
printfformatstring is the \0 terminated string to use as in the standard C printf routine
... are the parameters that are used by the format string
Example: ACTIVEprintf ( 4, "%d: %d", index, data); // Displays "23: 15432" on channel 4 if index = 23 and data = 15432
ACTIVEValue ( unsigned char channel, signed long value );
This routine outputs the given value on the Channel specified to be graphed over time.
channel = 0 thru 63
value is the value to output on the graph. value is a signed long and can therefore range from –2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647
Example: ACTIVEValue ( 2, ADCValue ); // Adds a graphed point at the value 123 on channel 2 at the current time if ADCValue = 123
ACTIVELabel( unsigned char channel, unsigned char * string );
This routine sets the label for the Channel specified.
channel = 0 thru 63
string is the \0 terminated string that becomes the new channel label.
Example: ACTIVELabel( 2, "State"); // Changes the Channel 2 label to "State"
Control Commands
These commands are sent using the string parameter in the call to ACTIVE-PROText().
Play Beep: ACTIVEText( channel, "?cmd=beep");
This command generates an audible BEEP on the computer when it is sent.
channel = 0 thru 7, ignored
Example: ACTIVEText( 2, "?cmd=beep"); // plays a beep on the computer
Stop Capture: ACTIVEText( channel, "?cmd=stop");
This command stops the capture in progress and displays the trace that has been stored to disk.
channel = 0 thru 7, ignored
Example: ACTIVEText( 2, "?cmd=stop"); // stops the capture
Restart Capture: ACTIVEText( channel, "?cmd=restart");
This command stops and restarts the capture. This discards the trace that was previously stored to disk.
channel = 0 thru 7, ignored
Example: ACTIVEText( 2, "?cmd=restart"); // stops and restarts the capture, discarding the previous trace.
Embedded Firmware
A key component to the Active-Pro™ system is the firmware that runs on your embedded microcontroller. The microcontroller sends debug information out a pair of general purpose I/O lines (GPIO) whenever you want to see a state, location or variable of your code in real-time operation. To send out this data you call one of 3 API routines that we provide below.
The firmware source code below is embedded in your firmware project and provides simple API routines that can be called any time your firmware wants to output information. Similar to printf(...), you can quickly add single lines of code to output a new set of information at exactly the correct time.
To use this firmware source code, copy the source into your project (either inline or in a new source file). Then modify the contents between the MAKE YOUR CHANGES comments. These modifications define how to set the output level of the two GPIO signals as well as other platform specific settings. See the source code comments below for more details.
Source Code in C
The following is the source code to include in your firmware project. The following code shows how to call the routines from your application. You need to first call ACTIVEInit() at the beginning of your application. You can then place ACTIVEText, ACTIVEValue or ACTIVEprintf() calls wherever you need to output a debug string or value.
#include <Wire.h>
#include "active.h"
#include "SparkFun_BMA400_Arduino_Library.h"
// Create a new sensor object
BMA400 accelerometer;
// I2C address selection
uint8_t i2cAddress = BMA400_I2C_ADDRESS_DEFAULT; // 0x14
void setup()
{
ACTIVEInit(); // Call this routine to configure any hardware used by the ACTIVE Bus
ACTIVEText( 0, "Hello World" ); // Debug Text Output
// Initialize the I2C library
Wire.begin();
// Check if sensor is connected and initialize
while(accelerometer.beginI2C(i2cAddress) != BMA400_OK)
{
// Wait a bit to see if connection is established
delay(1000);
}
}
void loop()
{
// Get measurements from the sensor
accelerometer.getSensorData();
// Send the values to the Active-Pro Firmware Debugger
ACTIVEValue( 1, accelerometer.data.accelX * 100);
ACTIVEValue( 2, accelerometer.data.accelY * 100);
ACTIVEValue( 3, accelerometer.data.accelZ * 100);
}
Output of the above code showing the ACTIVEText and ACTIVEValue debug outputs
ACTIVE.C
/* =============================================================
ACTIVE-PRO Firmware Debugger
Debug Output Routines
Provided by activefirmwaretools.com
This file is to be included in your embedded firmware project to
send debug information to the ACTIVE-PRO Firmware Debugger.
If you have any questions or issues, please email us at
support@activefirmwaretools.com.
===============================================================*/
#define ACTIVE_DEBUG_ON // Comment this line out to remove all ACTIVE Debug output from your project
//===============================================================================================
// MAKE MODIFICATIONS FOR YOUR HARDWARE SETUP BELOW THIS LINE
//===============================================================================================
// CHANGE #1: Add any includes that you need for the interface to your hardware to the ACTIVE bus
#include "project.h" // for PSoC Projects
// CHANGE #2: Modify this routine to set up the interface from this processor to the ACTIVE bus
void ACTIVEInit( void )
{
// Setup your hardware components for the ACTIVE Debug interface. Uncomment the mode you want to use or create your own
// based on the processor you are using.
// 1-Wire UART Interface
// Serial.begin(3000000, SERIAL_8N1, -1, 1); // Use IO1 as the output signal at 3MBaud, No parity, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit (Arduino Style)
// UART_Start(); // Setup the UART Hardware Block (PSoC Style)
// 2-wire SPI Interface
// SPI.begin(18, -1, 19); // Initialize the SPI block and assign pins
// SPI.setFrequency(40000000); // Set the SPI SCK frequency to 40MHz
SPI_Start(); // Setup the SPI hardware block (PSoC Style)
// 2-wire GPIO Interface
// pinMode(CLOCK_PIN, OUTPUT); // Set the CLOCK to an Output (Arduino Style)
// pinMode(DATA_PIN, OUTPUT); // Set the DATA to an Output (Arduino Style)
//ACTIVE_CLOCK_GPIO_SetDriveMode( PIN_DM_STRONG ); // Set the CLOCK to an Output (PSoC Style)
//ACTIVE_DATA_GPIO_SetDriveMode( PIN_DM_STRONG ); // Set the DATA to an Output (PSoC Style)
// SWV Interface (UART Mode Only 8,N,1)
// SWV_Start(); // Setup the SWV hardware (PSoC Style). Replace this with your processors SWV setup routine.
}
// CHANGE #3: Modify this routine to send an array of bytes to the the ACTIVE Debug Interface
void SendACTIVEPacket( unsigned char *data, int length ) // This routine is used to send a packet to the ACTIVE Debug Interface
{
// Send the packet out the wires. Choose the one type you have selected for this processor.
// 2-wire SPI Interface
// SPI.writeBytes( data, length ); // Send the packet directly to the SPI hardware (ESP32 Arduino version)
SPI_PutArray( data, length );
// 1-wire UART Interface
// Serial.write( data, length ); // Send the packet directly to the UART hardware (ESP32 Arduino version)
// UART_PutArray( data, length ); // Send the packet directly to the UART hardware (PSoC version)
// 2-wire GPIO Interface
// unsigned char value;
// while(length--)
// {
// // Send the next byte of data
// value = *data++;
// // Set the DATA line, and toggle the CLOCK for each bit, MSbit first (PSoC Style)
// // Replace the calls here for your calls to set the GPIO output level of the DATA and CLOCK lines.
//
// if (value & 0x80) ACTIVE_DATA_GPIO_Write(1); else ACTIVE_DATA_GPIO_Write(0); ACTIVE_CLOCK_GPIO_Write(1); ACTIVE_CLOCK_GPIO_Write(0);
// if (value & 0x40) ACTIVE_DATA_GPIO_Write(1); else ACTIVE_DATA_GPIO_Write(0); ACTIVE_CLOCK_GPIO_Write(1); ACTIVE_CLOCK_GPIO_Write(0);
// if (value & 0x20) ACTIVE_DATA_GPIO_Write(1); else ACTIVE_DATA_GPIO_Write(0); ACTIVE_CLOCK_GPIO_Write(1); ACTIVE_CLOCK_GPIO_Write(0);
// if (value & 0x10) ACTIVE_DATA_GPIO_Write(1); else ACTIVE_DATA_GPIO_Write(0); ACTIVE_CLOCK_GPIO_Write(1); ACTIVE_CLOCK_GPIO_Write(0);
// if (value & 0x08) ACTIVE_DATA_GPIO_Write(1); else ACTIVE_DATA_GPIO_Write(0); ACTIVE_CLOCK_GPIO_Write(1); ACTIVE_CLOCK_GPIO_Write(0);
// if (value & 0x04) ACTIVE_DATA_GPIO_Write(1); else ACTIVE_DATA_GPIO_Write(0); ACTIVE_CLOCK_GPIO_Write(1); ACTIVE_CLOCK_GPIO_Write(0);
// if (value & 0x02) ACTIVE_DATA_GPIO_Write(1); else ACTIVE_DATA_GPIO_Write(0); ACTIVE_CLOCK_GPIO_Write(1); ACTIVE_CLOCK_GPIO_Write(0);
// if (value & 0x01) ACTIVE_DATA_GPIO_Write(1); else ACTIVE_DATA_GPIO_Write(0); ACTIVE_CLOCK_GPIO_Write(1); ACTIVE_CLOCK_GPIO_Write(0);
// }
// SWV Interface (UART Mode Only 8,N,1)
// while(length--) ITM_SendChar( *data++ ); // Send the packet directly to the SWV Hardware Block (PSoC version)
}
//===============================================================================================
// MAKE MODIFICATIONS FOR YOUR HARDWARE SETUP ABOVE THIS LINE ONLY
//===============================================================================================
//===============================================================================================
// Define the basic Value and Text ACTIVE Message transmit routines
//===============================================================================================
#ifdef ACTIVE_DEBUG_ON
#define MAX_ACTIVE_LENGTH 255 // This defines the maximum length of any debug message
unsigned char ACTIVETxBuffer[MAX_ACTIVE_LENGTH]; // Holds the debug packet as it is being built
void ACTIVEValue( int channel, int value )
{
int length = 0;
char done = 0;
char positive = (value >= 0);
// Assemble the ACTIVE Value Packet
ACTIVETxBuffer[length++] = 0x7F; // Every ACTIVE packet starts with a 0x7F
ACTIVETxBuffer[length++] = channel & 0x3F; // Type and Channel: Bit 7=0, Bit 6=0 Means Value, Bits 5:0 means the channel (0-63)
while(!done)
{
if ((positive && (value >= 32)) || (!positive && (value < -32)))
{
ACTIVETxBuffer[length++] = value & 0x3F;
value = value >> 6;
}
else
{
ACTIVETxBuffer[length++] = (value & 0x3F ) | 0x40;
done = 1;
}
}
// Now actually send the packet to the Active-Pro
SendACTIVEPacket(ACTIVETxBuffer, length);
}
void ACTIVEText( int channel, char *string )
{
int length = 0;
ACTIVETxBuffer[length++] = 0x7F; // Every ACTIVE packet starts with a 0x7F
ACTIVETxBuffer[length++] = 0x40 | (channel & 0x3F); // Type and Channel: Bit 7=0, Bit 6=1 Means Text, Bits 5:0 means the channel (0-63)
while(*string)
{
if (length >= MAX_ACTIVE_LENGTH-1)
break;
ACTIVETxBuffer[length++] = *string & 0x7F; // Send the ascii characters
string++;
}
ACTIVETxBuffer[length++] = 0; // Send the string termination
// Now actually send the packet to the Active-Pro
SendACTIVEPacket(ACTIVETxBuffer, length);
}
//===============================================================================================
// Define the printf-like ACTIVE message routine
//===============================================================================================
#include "stdio.h"
#include <stdarg.h> // va_list, va_start, and va_end
char ACTIVEstr[MAX_ACTIVE_LENGTH];
void ACTIVEprintf( int channel, char *format, ... )
{
va_list arglist;
va_start( arglist, format );
vsprintf( ACTIVEstr, format, arglist );
va_end( arglist );
ACTIVEText( channel, ACTIVEstr );
};
#else // ACTIVE Debug is turned off, so make empty stubs for all routines
void ACTIVEInit( void ) {};
void ACTIVEText( int channel, char *string ) {};
void ACTIVEValue( int channel, int value ) {};
void ACTIVEprintf( int channel, char *format, ... ) {};
#endif
ACTIVE.H
#ifndef ACTIVE_DEBUG_H #define ACTIVE_DEBUG_H void ACTIVEInit( void ); // Initialize any hardware needed by the ACTIVE Interface void ACTIVEValue( int channel, int value ); // Output a Value for this channel void ACTIVEText( int channel, char *string ); // Output Text for this channel void ACTIVEprintf( int channel, char *format, ... ); // printf-like function with variable argument list // Define helpful macros for sending debug command messages #define ACTIVELabel(channel,string) ACTIVEText( (channel) , "?cmd=label&label=" string ) #define ACTIVEBeep() ACTIVEText( 0 , "?cmd=beep" ) #define ACTIVEStop() ACTIVEText( 0 , "?cmd=stop" ) #define ACTIVERestart() ACTIVEText( 0 , "?cmd=restart" ) #endif
Source Code in Verilog
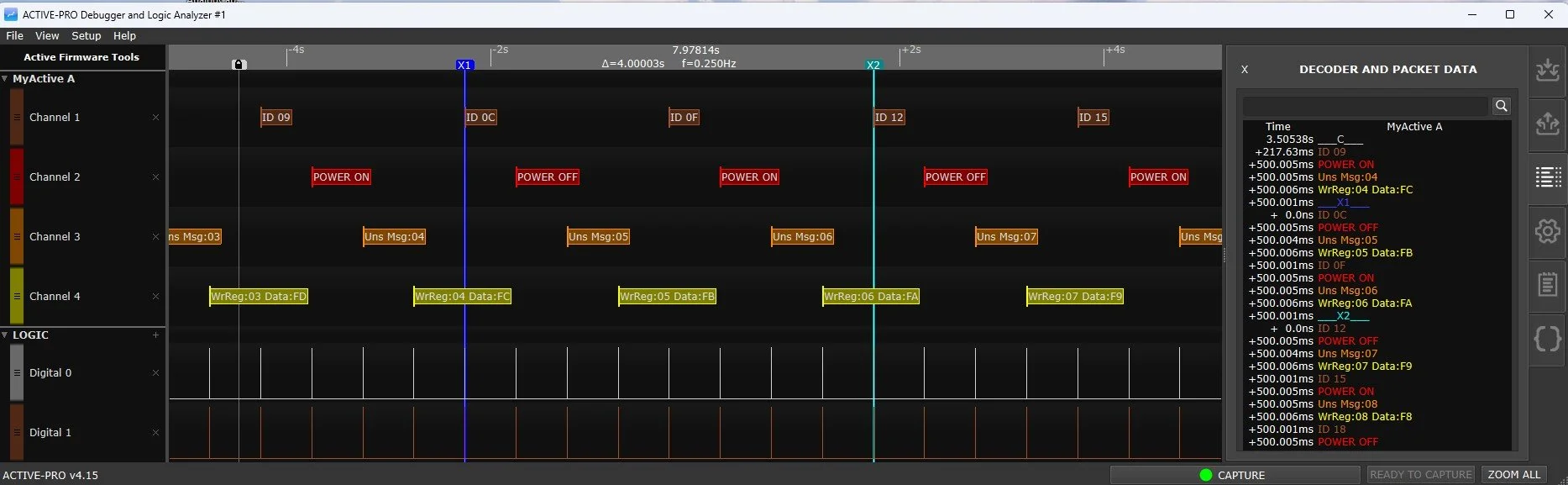
Below is an example Verilog (SystemVerilog) example that sends 4 example debug messages from your verilog RTL. The output of this code on the Active-Pro looks like this:
//===================================================================================
// Example Top module - replace with your code.
//
// This shows how to instantiate the ACTIVEPRO module and use it in your RTL.
//===================================================================================
module top (
input clock,
input reset_n,
// Active-Pro output pins
output active_clock,
output active_data
);
//===================================================================================
// Instantiate the Active Debug Port Output module
//===================================================================================
// Active-Pro Debug registers (written by this example, consumed by ACTIVEPRO)
reg [511:0] active_message;
reg [5:0] active_channel;
reg active_wr;
// Active Debug Port serializer/packetizer
ACTIVEPRO myactivepro (
.reset_n (reset_n),
.clock (clock), // Output clock is half this clock
.active_data (active_data), // Active Debug Port Output Data
.active_clock (active_clock), // Active Debug Port Output Clock
.message (active_message), // 0 (zero) surrounded debug text message
.channel (active_channel), // Active Debug Port channel to use
.wr (active_wr) // Write strobe
);
//===================================================================================
// Simulate strobes and variables that trigger Debug output messages.
//===================================================================================
reg send_unsolicited_message;
reg [7:0] unsolicited_id;
reg write_strobe;
reg [7:0] write_register;
reg [7:0] write_data;
reg kiv_rx_fifo_rd;
reg [7:0] kiv_rx_packet_id;
reg power_on;
reg old_power_on;
reg [31:0] my_counter;
always @(posedge clock) begin
if (!reset_n) begin
power_on <= 1'b0;
send_unsolicited_message <= 1'b0;
unsolicited_id <= 8'd0;
write_strobe <= 1'b0;
write_register <= 8'd0;
write_data <= 8'd0;
kiv_rx_fifo_rd <= 1'b0;
kiv_rx_packet_id <= 8'd0;
my_counter <= 32'd0;
end else begin
send_unsolicited_message <= 1'b0;
write_strobe <= 1'b0;
kiv_rx_fifo_rd <= 1'b0;
my_counter <= my_counter + 1;
if (my_counter == 30000000) begin
send_unsolicited_message <= 1'b1;
unsolicited_id <= unsolicited_id + 1;
end else if (my_counter == 60000000) begin
write_strobe <= 1'b1;
write_register <= write_register + 1;
write_data <= write_data - 1;
end else if (my_counter == 90000000) begin
kiv_rx_fifo_rd <= 1'b1;
kiv_rx_packet_id <= kiv_rx_packet_id + 3;
end else if (my_counter == 120000000) begin
power_on <= !power_on;
my_counter <= 32'd0;
end
end
end
//===================================================================================
// Hex to ASCII lookup table
//===================================================================================
localparam logic [0:255][15:0] hextoa = {
"00","01","02","03","04","05","06","07","08","09","0A","0B","0C","0D","0E","0F",
"10","11","12","13","14","15","16","17","18","19","1A","1B","1C","1D","1E","1F",
"20","21","22","23","24","25","26","27","28","29","2A","2B","2C","2D","2E","2F",
"30","31","32","33","34","35","36","37","38","39","3A","3B","3C","3D","3E","3F",
"40","41","42","43","44","45","46","47","48","49","4A","4B","4C","4D","4E","4F",
"50","51","52","53","54","55","56","57","58","59","5A","5B","5C","5D","5E","5F",
"60","61","62","63","64","65","66","67","68","69","6A","6B","6C","6D","6E","6F",
"70","71","72","73","74","75","76","77","78","79","7A","7B","7C","7D","7E","7F",
"80","81","82","83","84","85","86","87","88","89","8A","8B","8C","8D","8E","8F",
"90","91","92","93","94","95","96","97","98","99","9A","9B","9C","9D","9E","9F",
"A0","A1","A2","A3","A4","A5","A6","A7","A8","A9","AA","AB","AC","AD","AE","AF",
"B0","B1","B2","B3","B4","B5","B6","B7","B8","B9","BA","BB","BC","BD","BE","BF",
"C0","C1","C2","C3","C4","C5","C6","C7","C8","C9","CA","CB","CC","CD","CE","CF",
"D0","D1","D2","D3","D4","D5","D6","D7","D8","D9","DA","DB","DC","DD","DE","DF",
"E0","E1","E2","E3","E4","E5","E6","E7","E8","E9","EA","EB","EC","ED","EE","EF",
"F0","F1","F2","F3","F4","F5","F6","F7","F8","F9","FA","FB","FC","FD","FE","FF"
};
always @(posedge clock) begin
if (!reset_n) begin
active_wr <= 1'b0;
active_message <= 512'd0;
active_channel <= 6'd0;
old_power_on <= 1'b0;
end else begin
active_wr <= 1'b0;
old_power_on <= power_on;
if (power_on != old_power_on) begin
if (power_on)
active_message <= {8'd0, "POWER ON", 8'd0};
else
active_message <= {8'd0, "POWER OFF", 8'd0};
active_channel <= 6'd2;
active_wr <= 1'b1;
end
if (send_unsolicited_message) begin
active_message <= {8'd0, "Uns Msg:", hextoa[unsolicited_id], 8'd0};
active_channel <= 6'd3;
active_wr <= 1'b1;
end
if (write_strobe) begin
active_message <= {
8'd0, "WrReg:", hextoa[write_register],
" Data:", hextoa[write_data], 8'd0
};
active_channel <= 6'd4;
active_wr <= 1'b1;
end
if (kiv_rx_fifo_rd) begin
active_message <= {8'd0, "ID ", hextoa[kiv_rx_packet_id], 8'd0};
active_channel <= 6'd1;
active_wr <= 1'b1;
end
end
end
endmodule
//===================================================================================
// Active-Pro Debug Output Module
//===================================================================================
module ACTIVEPRO (
input reset_n,
input clock,
output active_data,
output active_clock,
input [511:0] message,
input [5:0] channel,
input wr
);
reg [15:0] byte_to_send;
reg strobe;
reg [7:0] byte_data;
wire done;
byte_serial_shifter myshifter (
.reset_n (reset_n),
.clk (clock),
.strobe (strobe),
.byte_in (byte_data),
.out_clk (active_clock),
.out_data(active_data),
.done (done)
);
reg [7:0] length;
integer i;
reg counting;
always @* begin
length = 0;
counting = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 64; i = i + 1) begin
if (!counting) begin
if (message[i*8 +: 8] == 8'h00)
counting = 1;
end else begin
if (message[i*8 +: 8] == 8'h00)
counting = 0;
else
length = length + 1;
end
end
end
always @(posedge clock or negedge reset_n) begin
if (!reset_n) begin
byte_to_send <= 16'd0;
strobe <= 1'b0;
byte_data <= 8'h00;
end else begin
strobe <= 1'b0;
if (wr) begin
byte_to_send <= 16'd1;
end else if (byte_to_send && done && !strobe) begin
if (byte_to_send == 16'd1) begin
strobe <= 1'b1;
byte_data <= 8'h7F;
byte_to_send <= 16'd2;
end else if (byte_to_send == 16'd2) begin
strobe <= 1'b1;
byte_data <= {2'b01, channel};
byte_to_send <= 16'd3;
end else begin
strobe <= 1'b1;
byte_data <= message[((length - byte_to_send + 4) * 8) - 1 -: 8];
byte_to_send <= byte_to_send + 1;
if (byte_to_send == length + 3)
byte_to_send <= 16'd0;
end
end
end
end
endmodule
//===================================================================================
// Byte Serial Shifter
//===================================================================================
module byte_serial_shifter (
input wire reset_n,
input wire clk,
input wire strobe,
input wire [7:0] byte_in,
output reg out_clk,
output reg out_data,
output wire done
);
reg busy;
reg [7:0] shreg;
reg [2:0] bit_idx;
reg phase;
assign done = ~busy;
always @(posedge clk or negedge reset_n) begin
if (!reset_n) begin
busy <= 1'b0;
shreg <= 8'h00;
bit_idx <= 3'd0;
phase <= 1'b0;
out_clk <= 1'b0;
out_data <= 1'b0;
end else begin
if (!busy) begin
out_clk <= 1'b0;
phase <= 1'b0;
if (strobe) begin
busy <= 1'b1;
shreg <= byte_in;
bit_idx <= 3'd7;
out_data <= byte_in[7];
end
end else begin
if (!phase) begin
out_clk <= 1'b1;
phase <= 1'b1;
end else begin
out_clk <= 1'b0;
phase <= 1'b0;
if (bit_idx == 0) begin
busy <= 1'b0;
end else begin
bit_idx <= bit_idx - 1;
shreg <= {shreg[6:0], 1'b0};
out_data <= shreg[6];
end
end
end
end
end
endmodule
Source Code in VHDL
-- =============================================================================
-- VHDL conversion of the provided Verilog file
-- =============================================================================
library ieee;
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
use ieee.numeric_std.all;
-- =============================================================================
-- Helpers (ASCII packing + hex rendering)
-- =============================================================================
package activepro_utils is
function ascii_vec(s : string) return std_logic_vector;
function zext512(v : std_logic_vector) return std_logic_vector;
function nibble_to_ascii(n : std_logic_vector(3 downto 0)) return std_logic_vector;
function byte_to_hex_ascii(b : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0)) return std_logic_vector; -- 16 bits (two chars)
end package;
package body activepro_utils is
function ascii_vec(s : string) return std_logic_vector is
variable v : std_logic_vector(s'length*8-1 downto 0);
variable k : integer := 0;
variable c : integer;
begin
-- Pack string left-to-right into increasing byte order (LSB = first char)
-- v(7 downto 0) = s(s'low), v(15 downto 8) = next char, etc.
for i in s'range loop
c := character'pos(s(i));
v(k*8+7 downto k*8) := std_logic_vector(to_unsigned(c, 8));
k := k + 1;
end loop;
return v;
end function;
function zext512(v : std_logic_vector) return std_logic_vector is
variable r : std_logic_vector(511 downto 0) := (others => '0');
begin
if v'length > 0 then
r(v'length-1 downto 0) := v;
end if;
return r;
end function;
function nibble_to_ascii(n : std_logic_vector(3 downto 0)) return std_logic_vector is
variable u : unsigned(3 downto 0) := unsigned(n);
variable c : unsigned(7 downto 0);
begin
if u < 10 then
c := to_unsigned(character'pos('0') + to_integer(u), 8);
else
c := to_unsigned(character'pos('A') + (to_integer(u) - 10), 8);
end if;
return std_logic_vector(c);
end function;
function byte_to_hex_ascii(b : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0)) return std_logic_vector is
variable hi : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0);
variable lo : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0);
variable r : std_logic_vector(15 downto 0);
begin
hi := nibble_to_ascii(b(7 downto 4));
lo := nibble_to_ascii(b(3 downto 0));
r(7 downto 0) := hi; -- first char in lower byte (matches ascii_vec packing)
r(15 downto 8) := lo; -- second char in next byte
return r;
end function;
end package body;
-- =============================================================================
-- Byte Serial Shifter
-- =============================================================================
entity byte_serial_shifter is
port (
reset_n : in std_logic;
clk : in std_logic;
strobe : in std_logic;
byte_in : in std_logic_vector(7 downto 0);
out_clk : out std_logic;
out_data : out std_logic;
done : out std_logic
);
end entity;
architecture rtl of byte_serial_shifter is
signal busy : std_logic := '0';
signal shreg : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0) := (others => '0');
signal bit_idx : unsigned(2 downto 0) := (others => '0');
signal phase : std_logic := '0'; -- 0 = clock low phase, 1 = clock high phase
signal out_clk_r : std_logic := '0';
signal out_data_r : std_logic := '0';
begin
out_clk <= out_clk_r;
out_data <= out_data_r;
done <= not busy;
process(clk, reset_n)
begin
if reset_n = '0' then
busy <= '0';
shreg <= (others => '0');
bit_idx <= (others => '0');
phase <= '0';
out_clk_r <= '0';
out_data_r <= '0';
elsif rising_edge(clk) then
if busy = '0' then
-- IDLE: clock is not toggling
out_clk_r <= '0';
phase <= '0';
if strobe = '1' then
busy <= '1';
shreg <= byte_in;
bit_idx <= to_unsigned(7, 3);
-- Put first bit on the line before the first rising edge
out_data_r <= byte_in(7);
end if;
else
-- ACTIVE: clock toggles only as part of bit timing
if phase = '0' then
-- create the rising edge for this bit
out_clk_r <= '1';
phase <= '1';
else
-- create the falling edge, then advance
out_clk_r <= '0';
phase <= '0';
if bit_idx = 0 then
-- last bit is complete; stop toggling clock
busy <= '0';
else
bit_idx <= bit_idx - 1;
shreg <= shreg(6 downto 0) & '0';
-- next bit is valid during the following low phase
out_data_r <= shreg(6);
end if;
end if;
end if;
end if;
end process;
end architecture;
-- =============================================================================
-- ACTIVEPRO Debug Output Module
-- =============================================================================
entity ACTIVEPRO is
port (
reset_n : in std_logic;
clock : in std_logic;
active_data : out std_logic;
active_clock : out std_logic;
message : in std_logic_vector(511 downto 0);
channel : in std_logic_vector(5 downto 0);
wr : in std_logic
);
end entity;
architecture rtl of ACTIVEPRO is
signal byte_to_send : unsigned(15 downto 0) := (others => '0');
signal strobe : std_logic := '0';
signal byte_data : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0) := (others => '0');
signal done : std_logic;
signal length : unsigned(7 downto 0) := (others => '0');
signal counting : std_logic := '0';
-- message byte slice helper (byte index i: bits i*8+7 downto i*8)
function msg_byte(msg : std_logic_vector(511 downto 0); i : integer) return std_logic_vector is
variable b : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0);
begin
b := msg(i*8+7 downto i*8);
return b;
end function;
begin
-- Serializer
u_shifter : entity work.byte_serial_shifter
port map (
reset_n => reset_n,
clk => clock,
strobe => strobe,
byte_in => byte_data,
out_clk => active_clock,
out_data => active_data,
done => done
);
-- Find message length (counts bytes between first 0x00 and second 0x00)
process(message)
variable len_v : unsigned(7 downto 0);
variable cnt_v : std_logic;
variable i : integer;
variable b : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0);
begin
len_v := (others => '0');
cnt_v := '0';
for i in 0 to 63 loop
b := msg_byte(message, i);
if cnt_v = '0' then
if b = x"00" then
cnt_v := '1';
end if;
else
if b = x"00" then
cnt_v := '0'; -- stop counting, but keep looping
else
len_v := len_v + 1;
end if;
end if;
end loop;
length <= len_v;
counting <= cnt_v;
end process;
-- Active Debug Port Message Sender
process(clock, reset_n)
variable sel_msb : integer;
variable sel_lsb : integer;
variable expr : integer;
begin
if reset_n = '0' then
byte_to_send <= (others => '0');
strobe <= '0';
byte_data <= x"00";
elsif rising_edge(clock) then
-- Default: no new byte launch unless we decide to send one below
strobe <= '0';
-- wr arms the sender (starts at byte_to_send=1 => header byte 0)
if wr = '1' then
byte_to_send <= to_unsigned(1, 16);
else
-- Launch next byte only when in a send sequence and shifter idle
if (byte_to_send /= 0) and (done = '1') and (strobe = '0') then
if byte_to_send = to_unsigned(1, 16) then
strobe <= '1';
byte_data <= x"7F"; -- Header byte 0
byte_to_send <= to_unsigned(2, 16);
elsif byte_to_send = to_unsigned(2, 16) then
strobe <= '1';
byte_data <= "01" & channel; -- Header byte 1: 2-bit type + 6-bit channel
byte_to_send <= to_unsigned(3, 16);
else
-- Payload bytes pulled from "message" using the same indexing scheme as Verilog:
-- message[((length - byte_to_send + 4)*8)-1 -: 8]
strobe <= '1';
expr := (to_integer(length) - to_integer(byte_to_send) + 4);
sel_msb := expr * 8 - 1;
sel_lsb := sel_msb - 7;
byte_data <= message(sel_msb downto sel_lsb);
byte_to_send <= byte_to_send + 1;
-- End after message sent + 2 header bytes + ending 0
if byte_to_send = to_unsigned(to_integer(length) + 3, 16) then
byte_to_send <= (others => '0');
end if;
end if;
end if;
end if;
end if;
end process;
end architecture;
-- =============================================================================
-- Example Top module
-- =============================================================================
entity top is
port (
clock : in std_logic;
reset_n : in std_logic;
active_clock : out std_logic;
active_data : out std_logic
);
end entity;
architecture rtl of top is
use work.activepro_utils.all;
signal active_message : std_logic_vector(511 downto 0) := (others => '0');
signal active_channel : std_logic_vector(5 downto 0) := (others => '0');
signal active_wr : std_logic := '0';
signal send_unsolicited_message : std_logic := '0';
signal unsolicited_id : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0) := (others => '0');
signal write_strobe : std_logic := '0';
signal write_register : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0) := (others => '0');
signal write_data : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0) := (others => '0');
signal kiv_rx_fifo_rd : std_logic := '0';
signal kiv_rx_packet_id : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0) := (others => '0');
signal power_on : std_logic := '0';
signal old_power_on : std_logic := '0';
signal my_counter : unsigned(31 downto 0) := (others => '0');
begin
u_activepro : entity work.ACTIVEPRO
port map (
reset_n => reset_n,
clock => clock,
active_data => active_data,
active_clock => active_clock,
message => active_message,
channel => active_channel,
wr => active_wr
);
-- Stimulus generator (example)
process(clock)
begin
if rising_edge(clock) then
if reset_n = '0' then
power_on <= '0';
send_unsolicited_message <= '0';
unsolicited_id <= (others => '0');
write_strobe <= '0';
write_register <= (others => '0');
write_data <= (others => '0');
kiv_rx_fifo_rd <= '0';
kiv_rx_packet_id <= (others => '0');
my_counter <= (others => '0');
else
send_unsolicited_message <= '0';
write_strobe <= '0';
kiv_rx_fifo_rd <= '0';
my_counter <= my_counter + 1;
if my_counter = to_unsigned(30000000, 32) then
send_unsolicited_message <= '1';
unsolicited_id <= std_logic_vector(unsigned(unsolicited_id) + 1);
elsif my_counter = to_unsigned(60000000, 32) then
write_strobe <= '1';
write_register <= std_logic_vector(unsigned(write_register) + 1);
write_data <= std_logic_vector(unsigned(write_data) - 1);
elsif my_counter = to_unsigned(90000000, 32) then
kiv_rx_fifo_rd <= '1';
kiv_rx_packet_id <= std_logic_vector(unsigned(kiv_rx_packet_id) + 3);
elsif my_counter = to_unsigned(120000000, 32) then
power_on <= not power_on;
my_counter <= (others => '0');
end if;
end if;
end if;
end process;
-- Centralized debug message generator
process(clock)
variable v_msg : std_logic_vector(511 downto 0);
variable v : std_logic_vector(0 downto 0);
begin
if rising_edge(clock) then
if reset_n = '0' then
active_wr <= '0';
active_message <= (others => '0');
active_channel <= (others => '0');
old_power_on <= '0';
else
active_wr <= '0';
old_power_on <= power_on;
-- Example #4: message on power_on toggle
if power_on /= old_power_on then
if power_on = '1' then
active_message <= zext512(x"00" & ascii_vec("POWER ON") & x"00");
else
active_message <= zext512(x"00" & ascii_vec("POWER OFF") & x"00");
end if;
active_channel <= std_logic_vector(to_unsigned(2, 6));
active_wr <= '1';
end if;
-- Example #1: unsolicited message with 1 byte rendered as two hex chars
if send_unsolicited_message = '1' then
active_message <= zext512(
x"00" &
ascii_vec("Uns Msg:") &
byte_to_hex_ascii(unsolicited_id) &
x"00"
);
active_channel <= std_logic_vector(to_unsigned(3, 6));
active_wr <= '1';
end if;
-- Example #2: register write message
if write_strobe = '1' then
active_message <= zext512(
x"00" &
ascii_vec("WrReg:") &
byte_to_hex_ascii(write_register) &
ascii_vec(" Data:") &
byte_to_hex_ascii(write_data) &
x"00"
);
active_channel <= std_logic_vector(to_unsigned(4, 6));
active_wr <= '1';
end if;
-- Example #3: FIFO read message
if kiv_rx_fifo_rd = '1' then
active_message <= zext512(
x"00" &
ascii_vec("ID ") &
byte_to_hex_ascii(kiv_rx_packet_id) &
x"00"
);
active_channel <= std_logic_vector(to_unsigned(1, 6));
active_wr <= '1';
end if;
end if;
end if;
end process;
end architecture;
Source Code in Python
# =============================================================
# ACTIVE-PRO Firmware Debugger
# Debug Output Routines
# Provided by activefirmwaretools.com
#
# This file is to be included in your embedded firmware project to
# send debug information to the ACTIVE-PRO Firmware Debugger.
#
# If you have any questions or issues, please email us at
# support@activefirmwaretools.com.
# =============================================================
# Define ACTIVE_DEBUG_ON to enable debug output
ACTIVE_DEBUG_ON = True
if ACTIVE_DEBUG_ON:
import spidev
import serial
# Setup your hardware components for the ACTIVE Debug interface
def ACTIVEInit():
global spi, uart
spi = spidev.SpiDev()
spi.open(0, 0) # Adjust bus and device as per your setup
spi.max_speed_hz = 40000000
uart = serial.Serial()
uart.baudrate = 3000000
uart.port = '/dev/ttyS0' # Adjust as per your setup
uart.open()
# Send an array of bytes to the ACTIVE Debug Interface
def SendACTIVEPacket(data):
# Send the packet out the wires
# 2-wire SPI Interface
spi.xfer2(data)
# 1-wire UART Interface
uart.write(bytearray(data))
MAX_ACTIVE_LENGTH = 255 # This defines the maximum length of any debug message
ACTIVETxBuffer = bytearray(MAX_ACTIVE_LENGTH) # Holds the debug packet as it is being built
def ACTIVEValue(channel, value):
length = 0
done = False
positive = value >= 0
# Assemble the ACTIVE Value Packet
ACTIVETxBuffer[length] = 0x7F
length += 1
ACTIVETxBuffer[length] = channel & 0x3F # Type and Channel
length += 1
while not done:
if (positive and value >= 32) or (not positive and value < -32):
ACTIVETxBuffer[length] = value & 0x3F
value >>= 6
length += 1
else:
ACTIVETxBuffer[length] = (value & 0x3F) | 0x40
done = True
length += 1
# Now actually send the packet to the Active-Pro
SendACTIVEPacket(ACTIVETxBuffer[:length])
def ACTIVEText(channel, string):
length = 0
ACTIVETxBuffer[length] = 0x7F
length += 1
ACTIVETxBuffer[length] = 0x40 | (channel & 0x3F)
length += 1
for char in string:
if length >= MAX_ACTIVE_LENGTH - 1:
break
ACTIVETxBuffer[length] = ord(char) & 0x7F
length += 1
ACTIVETxBuffer[length] = 0 # Send the string termination
length += 1
# Now actually send the packet to the Active-Pro
SendACTIVEPacket(ACTIVETxBuffer[:length])
def ACTIVEprintf(channel, format_string, *args):
ACTIVEstr = format_string % args
ACTIVEText(channel, ACTIVEstr)
else:
# ACTIVE Debug is turned off, so make empty stubs for all routines
def ACTIVEInit():
pass
def ACTIVEText(channel, string):
pass
def ACTIVEValue(channel, value):
pass
def ACTIVEprintf(channel, format_string, *args):
pass